OCR is used for extracting text data from images. We discussed TesseractOCR for extracting text from different kind of images in our previous post. There are other options also available like easyocr, paddle paddle and different other tools. So in this tutorial we will use EasyOCR for extracting text data from images.
EasyOCR supports 80+ languages and all popular writing scripts including Latin, Chinese, Arabic, Devanagari, Cyrillic and etc. For complete details on language support and other options, check EasyOCR github page.
https://github.com/JaidedAI/EasyOCR
Installation
EasyOCR can be installed using pip easily on your system. It requires torch and torchvision installed before using EasyOCR so first need to install torch. Torch can be installed from pytorch website using pip and if you want to use GPU, use torch cuda version while installing. For more details check pytorch official page https://pytorch.org/. Now we can install easyocr on system.
# install using pip
pip install easyocr
# install from git (latest development release)
pip install git+git://github.com/jaidedai/easyocr.gitOnce installation is complete, we can use EasyOCR for character recognition. EasyOCR also provide docker file, check it out on github repo.
Usage
EasyOCR usage is very simple, on initialization we can specify a list of languages and also specify if GPU usage is required.
import easyocr
# specify languages and other configs
reader = easyocr.Reader(['en'])
# multiple languages (chinese, english)
reader = easyocr.Reader(['ch_sim','en'])
# no gpu
reader = easyocr.Reader(['ch_sim','en'], gpu=False)EasyOCR also offers to specify different languages in reader but not all languages can be used together. If you dont want to use GPU, set gpu=False in reader. If model for current configuration does not exist on system, it will download it from their repo, this process run only once.
Now we can input image to model and get results. It returns all detections with text output, bbox coordinates for text and confidence score.
# image path
result = reader.readtext('images/dpct0017.jpg')[([[69, 75], [944, 75], [944, 250], [69, 250]],
'September',
0.9998583346101947)]We can also input a numpy array, bytes or a url to fetch from web. Lets read image using opencv and provide as input to model.
Using OpenCV
Install opencv-python and then it can be used to read images and provide as input to easyocr and then also we can draw on image.
import cv2
image = cv2.imread('images/Pict0021.jpg') # read image
# perform character recognition
result = reader.readtext(image)
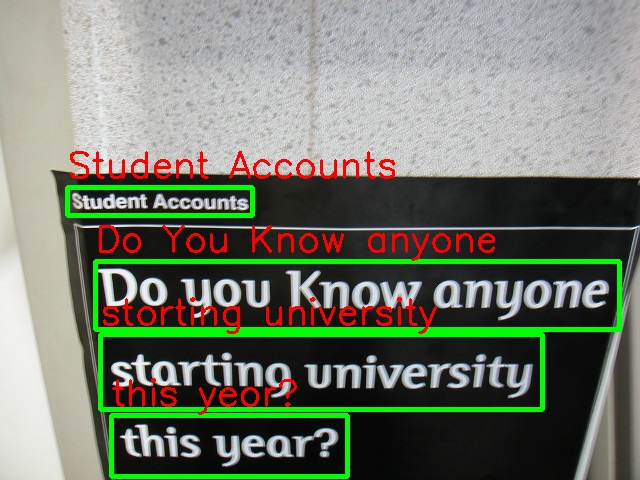
As it returns box coordinates, so we can draw on image using opencv methods.
# iterate on all results
for res in results:
top_left = tuple(res[0][0]) # top left coordinates as tuple
bottom_right = tuple(res[0][2]) # bottom right coordinates as tuple
# draw rectangle on image
cv2.rectangle(image, top_left, bottom_right, (0, 255, 0), 2)
# write recognized text on image (top_left) minus 10 pixel on y
cv2.putText(image, res[1], (top_left[0], top_left[1]-10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (0, 0, 255), 2) It can work for multiple words detection and drawing on image using this code.
It can work for multiple words detection and drawing on image using this code.
From URL
We can also provide image url input so it will fetch image and perform OCR automatically.
# provide image url instead of path
result = reader.readtext('https://i.stack.imgur.com/WiDpa.jpg')[([[19, 0], [897, 0], [897, 120], [19, 120]],
'The quick brown fox',
0.7889624100176502),
([[11, 113], [805, 113], [805, 229], [11, 229]],
'jumped over the 5',
0.9480686027185475),
([[13, 219], [469, 219], [469, 334], [13, 334]],
'lazy dogs!',
0.9391474148848226)]We can also provide detail=0 to get only text, if not interseted in coordinates and confidence score.
result = reader.readtext('https://i.stack.imgur.com/WiDpa.jpg', detail=0)['The quick brown fox', 'jumped over the 5', 'lazy dogs!']We can also iterate over a directory or bunch of images. Here are some other outputs from OCR model on different images and different environments.
import cv2
import os
for image_name in os.listdir("images"):
# read image
image = cv2.imread(f'images/{image_name}')
results = reader.readtext(image)
# draw rectangle on easyocr results
for res in results:
top_left = (int(res[0][0][0]), int(res[0][0][1])) # convert float to int
bottom_right = (int(res[0][2][0]), int(res[0][2][1])) # convert float to int
cv2.rectangle(image, top_left, bottom_right, (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.putText(image, res[1], (top_left[0], top_left[1]-10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1.2, (0, 0, 255), 2)
# write image
cv2.imwrite(f'output/{image_name}', image)
For more details on EasyOCR check Github repo or official documentation.

Comments (0)